SOCP - second order cone programming
minimizex fTx s.t.
||Aix+bi||2 ≤ ciTx+di, i=1,...,m
Fx = g,
where x ∈ Rn, f ∈ Rn, Ai ∈ RkiXn, bi ∈ Rki, ci ∈ Rn, di ∈ R and F ∈ RpXn
is called a second-order cone program (SOCP). See S.Boyd and L.Vandenberghe, "Convex Optimization", 4.4.2 for more details. The norm appearing in the constraints is the standard Euclidean norm, i.e., ||u||2 = (uTu)1/2.
We call a constraint of the form
||Ax+b||2 ≤ cTx+d,
where A ∈ RkXn, a second-order cone constraint of dimension k+1 because it is the same as requiring the affine function x→(Ax+b,cTx+d) from Rn to Rk+1 to lie in the second order cone in Rk+1. The second-order cone is also known by several other names: it is called the quadratic cone since it is defined by a quadratic inequality, or it is also called the Lorentz cone or ice-cream cone. The following image shows a second-order cone in R3:
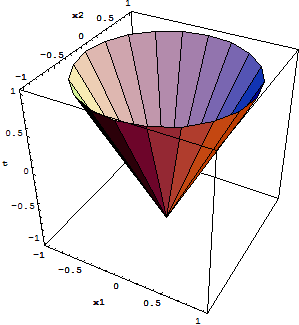
You can use the Barrier Method algorithm available with Solver4J for solving this type of problems, passing in the generalized barrier function for the second-order cone in Rk+1 as the barrier function (see S.Boyd and L.Vandenberghe, "Convex Optimization", p. 600):
with . For strictly feasible x the gradient is equal to
and the hessian is
where
, and
This function is represented in Solver4J with the class SOCPLogarithmicBarrier.2D example
Consider the problem graphically represented hereafter: 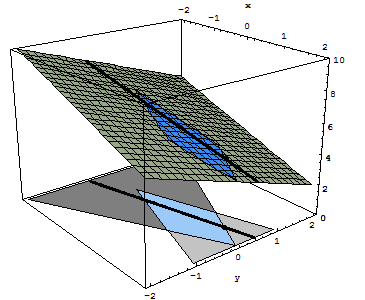
- the lightgrey cone, determined by:
- A1 = {{ 0, 1}}
- b1 = { 0 }
- c1 = { 1/3, 0}
- d1 = 1/3
- -x < 1
- the darkgrey cone, determined by:
- A2 = {{ 0, 1. }}
- b2 = {0}
- c2 = {-1/2, 0}
- d2 = 1
- x < 2
It can be solved like this:
// Objective function (plane)
double[] c = new double[] { -1., -1. };
LinearMultivariateRealFunction objectiveFunction = new LinearMultivariateRealFunction(c, 6);
//equalities
double[][] A = new double[][]{{1./4.,-1.}};
double[] b = new double[]{0};
List<SOCPConstraintParameters> socpConstraintParametersList = new ArrayList<SOCPLogarithmicBarrier.SOCPConstraintParameters>();
SOCPLogarithmicBarrier barrierFunction = new SOCPLogarithmicBarrier(socpConstraintParametersList, 2);
// second order cone constraint in the form ||A1.x+b1||<=c1.x+d1,
double[][] A1 = new double[][] {{ 0, 1. }};
double[] b1 = new double[] { 0 };
double[] c1 = new double[] { 1./3., 0. };
double d1 = 1./3.;
SOCPConstraintParameters constraintParams1 = barrierFunction.new SOCPConstraintParameters(A1, b1, c1, d1);
socpConstraintParametersList.add(socpConstraintParametersList.size(), constraintParams1);
// second order cone constraint in the form ||A2.x+b2||<=c2.x+d2,
double[][] A2 = new double[][] {{ 0, 1. }};
double[] b2 = new double[] { 0};
double[] c2 = new double[] { -1./2., 0};
double d2 = 1;
SOCPConstraintParameters constraintParams2 = barrierFunction.new SOCPConstraintParameters(A2, b2, c2, d2);
socpConstraintParametersList.add(socpConstraintParametersList.size(), constraintParams2);
//optimization problem
OptimizationRequest or = new OptimizationRequest();
or.setF0(objectiveFunction);
or.setInitialPoint(new double[] { 0., 0.});
or.setA(A);
or.setB(b);
or.setCheckProgressConditions(true);
//optimization
BarrierMethod opt = new BarrierMethod(barrierFunction);
opt.setOptimizationRequest(or);
opt.optimize();
double[] sol = opt.getOptimizationResponse().solution; sol[0] = 4/3 sol[1] = 1/3

