GP - geometric programming
s.t.
where are posynomials and are monomials, and (the constraint is implicit)
is called a (standard form) geometric program (GP). See S.Boyd and L.Vandenberghe, "Convex Optimization", 4.5.2 for more details.
We call a function with defined aswhere and a monomial function or simply a monomial; a sum of monomials, i.e. a function in the form
where is called a posynomial function with K terms, or simply a posynomial.
Geometric program are not convex optimization problems, but they can be transformed to convex problems by a change of variables and a transformation of the objective and constraint functions. So, using
a posynomial can be rewritten as
where and , and the GP defined above becomes:
s.t.
s.t.
2D example
Consider the problem graphically represented hereafter: 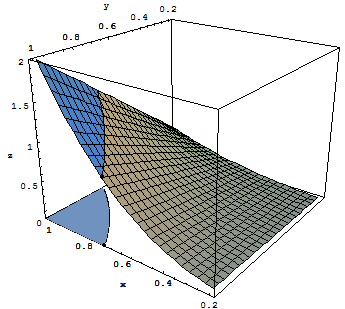
s.t.
// Objective function (variables (x,y), dim = 2)
double[] a01 = new double[]{2,1};
double b01 = 0;
double[] a02 = new double[]{3,1};
double b02 = 0;
ConvexMultivariateRealFunction objectiveFunction = new LogTransformedPosynomial(new double[][]{a01, a02}, new double[]{b01, b02});
//constraints
double[] a11 = new double[]{1,0};
double b11 = Math.log(1);
double[] a21 = new double[]{0,1};
double b21 = Math.log(1);
double[] a31 = new double[]{-1,-1.};
double b31 = Math.log(0.7);
ConvexMultivariateRealFunction[] inequalities = new ConvexMultivariateRealFunction[3];
inequalities[0] = new LogTransformedPosynomial(new double[][]{a11}, new double[]{b11});
inequalities[1] = new LogTransformedPosynomial(new double[][]{a21}, new double[]{b21});
inequalities[2] = new LogTransformedPosynomial(new double[][]{a31}, new double[]{b31});
//optimization problem
OptimizationRequest or = new OptimizationRequest();
or.setF0(objectiveFunction);
or.setFi(inequalities);
or.setInitialPoint(new double[]{Math.log(0.9), Math.log(0.9)});
//or.setInteriorPointMethod(Solver4J.BARRIER_METHOD);//if you prefer the barrier-method
//optimization
Solver4J opt = new Solver4J();
opt.setOptimizationRequest(or);
opt.optimize();
double[] sol = opt.getOptimizationResponse().solution; sol[0] = Math.log(0.7); sol[1] = Math.log(1);
x = -0.35667494 y = 0.0

