LFP - linear fractional programming
s.t.
with
is called a linear-fractional program (LFP). See S.Boyd and L.Vandenberghe, "Convex Optimization", 4.3.2 for more details.
Linear fractional programs are not convex optimization problems because the objective function is quasiconvex (quasilinear precisely) so linear-fractional programs are quasiconvex optimization problems; however, they can be transformed to convex problems by a change of variables and a transformation of the objective and constraint functions. If the feasible set
is notempty, LFP can be transformed to the equivalent LP
s.t.
2D example
Consider the problem graphically represented hereafter: 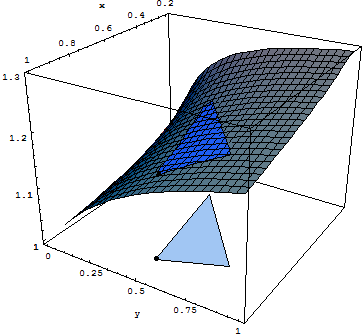
s.t.
and
It can be solved like this:
// Objective function (variables y0, y1, z)
double[] n = new double[] { 2., 4., 0.};
LinearMultivariateRealFunction objectiveFunction = new LinearMultivariateRealFunction(n, 0);
//inequalities (G.y-h.z<0, z>0)
double[][] Gmh = new double[][]{{-1.0, 1., 0.},
{ 3.0, 1.,-3.2},
{ 0.2,-1., 0.32},
{ 0.0, 0.,-1.0}};
ConvexMultivariateRealFunction[] inequalities = new ConvexMultivariateRealFunction[4];
for(int i=0; i<4;i++){
inequalities[i] = new LinearMultivariateRealFunction(Gmh[i], 0);
}
//equalities (e.y+f.z=1)
double[][] Amb = new double[][]{{ 2., 3., 0.}};
double[] bm= new double[]{1};
//optimization problem
OptimizationRequest or = new OptimizationRequest();
or.setF0(objectiveFunction);
or.setA(Amb);
or.setB(bm);
or.setFi(inequalities);
or.setTolerance(1.E-6);
or.setToleranceFeas(1.E-6);
//optimization
Solver4J opt = new Solver4J();
opt.setOptimizationRequest(or);
opt.optimize();
double[] sol = opt.getOptimizationResponse().solution; sol[0] = 0.2727; sol[1] = 0.1515; sol[2] = 0.3030;
x = 0,9 y = 0.5

