CCFP - convex-concave fractional programming
s.t.
where are convex and the domain of the objective function is defined as , is called a convex-concave-fractional program (CCFP). See S.Boyd and L.Vandenberghe, "Convex Optimization", p. 191 for more details.
Convex-concave fractional program is a quasiconvex optimization problem, but it can be shown that it is equivalent to the convex problem in the new variables :
s.t.
2D example
Consider the problem graphically represented hereafter: 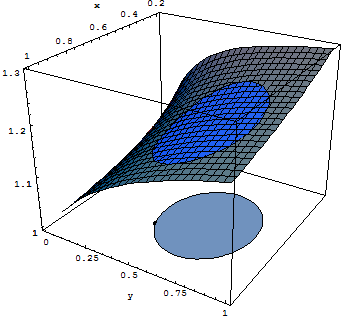
s.t.
It can be solved like this:
// Objective function (variables y0, y1, t)
double[] n = new double[] { 2., 4., 0.};
LinearMultivariateRealFunction objectiveFunction = new LinearMultivariateRealFunction(n, 0);
//inequalities
ConvexMultivariateRealFunction[] inequalities = new ConvexMultivariateRealFunction[2];
//t > 0
double[][] Gmh = new double[][]{{0.0, 0.0,-1.0}};//t>0
inequalities[0] = new LinearMultivariateRealFunction(Gmh[0], 0);
//perspective function of (x-c0)^2 + (y-c1)^2 - R^2 < 0
//this is t*((y0/t - c0)^2 + (y1/t - c1)^2 -R^2)
//we do not multiply by t, because it would make the function no more convex
final double c0 = 0.65;
final double c1 = 0.65;
final double R = 0.25;
inequalities[1] = new ConvexMultivariateRealFunction() {
public double value(DoubleMatrix1D X) {
double y0 = X.getQuick(0);
double y1 = X.getQuick(1);
double t = X.getQuick(2);
return t * (Math.pow(y0 / t - c0, 2) + Math.pow(y1 / t - c1, 2) - Math.pow(R, 2));
}
public DoubleMatrix1D gradient(DoubleMatrix1D X) {
double y0 = X.getQuick(0);
double y1 = X.getQuick(1);
double t = X.getQuick(2);
double[] ret = new double[3];
ret[0] = 2 * (y0/t - c0);
ret[1] = 2 * (y1/t - c1);
ret[2] = Math.pow(c0, 2) + Math.pow(c1, 2) - Math.pow(R, 2) - (Math.pow(y0, 2) + Math.pow(y1, 2))/Math.pow(t, 2);
return F1.make(ret);
}
public DoubleMatrix2D hessian(DoubleMatrix1D X) {
double y0 = X.getQuick(0);
double y1 = X.getQuick(1);
double t = X.getQuick(2);
double[][] ret = {
{ 2/t, 0, -2*y0/Math.pow(t,2)},
{ 0, 2/t, -2*y1/Math.pow(t,2)},
{-2*y0/Math.pow(t,2), -2*y1/Math.pow(t,2), 2*(Math.pow(y0,2) + Math.pow(y1,2))/Math.pow(t,3)}};
return F2.make(ret);
}
public int getDim() {
return 3;
}
};
//equalities (e.y+f.t=1), f is 0
double[][] Amb = new double[][]{{ 2., 3., 0.}};
double[] bm= new double[]{1};
//optimization problem
OptimizationRequest or = new OptimizationRequest();
or.setF0(objectiveFunction);
or.setA(Amb);
or.setB(bm);
or.setFi(inequalities);
or.setTolerance(1.E-6);
or.setToleranceFeas(1.E-6);
or.setNotFeasibleInitialPoint(new double[] { 0.6, -0.2/3., 0.1 });
or.setCheckKKTSolutionAccuracy(true);
//optimization
Solver4J opt = new Solver4J();
opt.setOptimizationRequest(or);
opt.optimize();
double[] sol = opt.getOptimizationResponse().solution; sol[0] = 0.2719; sol[1] = 0.1521; sol[2] = 0.3522;
x = 0.772 y = 0.431

